
Value Investing Strategy Explained sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with a clear and concise explanation of the core principles of value investing.
Readers will delve into the significance of intrinsic value, the analysis methods used by value investors for long-term gains, and much more.
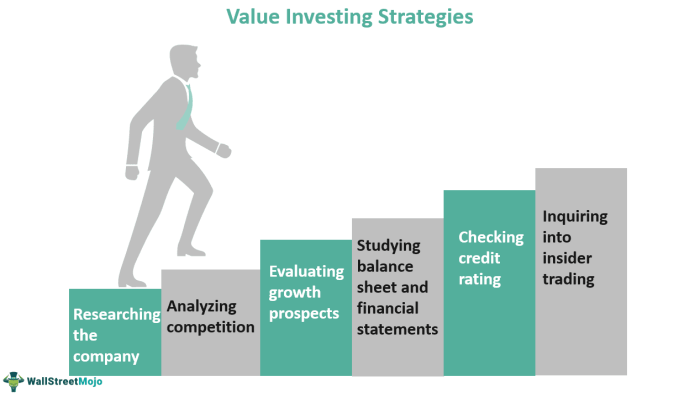
Value Investing Strategy Explained
Value investing is a strategy where investors actively seek stocks that they believe the market has undervalued. The core principle of value investing is to buy these undervalued stocks and hold them for the long term to benefit from their potential growth.
Importance of Intrinsic Value
In value investing, intrinsic value plays a crucial role in determining whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued. Intrinsic value is the true worth of a company’s stock, calculated based on its fundamentals such as earnings, assets, and growth potential. Value investors focus on buying stocks trading below their intrinsic value to maximize returns.
Analysis for Long-Term Gains
Value investors analyze stocks using various metrics such as price-to-earnings ratio, price-to-book ratio, and dividend yield to identify opportunities for long-term gains. By examining a company’s financial health, competitive position, and future prospects, value investors aim to make informed decisions that align with their investment goals.
Investment Advice
Investment advice from successful investors can provide valuable insights for individuals looking to grow their wealth through smart investment decisions. These experts have honed their strategies over years of experience and have shared key principles that can guide others in navigating the complex world of investing.
Role of Risk Management
Effective risk management is a cornerstone of sound investment advice. Successful investors understand that every investment carries a level of risk, and it is crucial to assess and mitigate these risks to protect capital and generate sustainable returns. By diversifying their portfolios, setting stop-loss orders, and conducting thorough research, investors can minimize downside risk and increase their chances of success in the market.
Importance of Diversification
Diversification is another key component of valuable investment advice. By spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions, investors can reduce the impact of volatility in any single investment. This strategy helps to cushion against losses and optimize returns over the long term. Through diversification, investors can create a balanced portfolio that offers stability and growth potential, even in challenging market conditions.
Investment Advisor
An investment advisor is a professional who provides guidance and advice to clients regarding their investment decisions. They help clients develop investment strategies that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Responsibilities of an Investment Advisor
- Assessing the financial situation and goals of clients
- Developing personalized investment plans
- Monitoring and adjusting investment portfolios
- Providing ongoing financial advice and guidance
- Keeping clients informed about market trends and developments
Creating Personalized Investment Plans
Investment advisors create personalized investment plans by first understanding their client’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. They then analyze various investment options and recommend a portfolio that aligns with the client’s objectives. This personalized approach helps clients achieve their financial goals while managing risks effectively.
Qualifications and Certifications
- To become an investment advisor, one typically needs a bachelor’s degree in finance, economics, or a related field.
- Many investment advisors also pursue certifications such as Certified Financial Planner (CFP) or Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) to enhance their credibility and expertise.
- Advisors are often required to pass licensing exams, such as the Series 65 exam, to legally provide investment advice.
- Continuing education is essential for investment advisors to stay up-to-date with industry trends and regulations.
Investment Banking
Investment banking plays a crucial role in the financial markets by facilitating the flow of capital between investors and corporations or governments. These institutions provide a range of financial services to help entities raise funds, manage assets, and execute complex financial transactions.
Difference Between Investment Banking and Commercial Banking
Investment banking primarily focuses on providing advisory services for mergers and acquisitions, underwriting securities offerings, and managing corporate finance activities. On the other hand, commercial banking focuses on traditional banking services like accepting deposits, providing loans, and managing individual and business accounts.
Services Offered by Investment Banks
- Underwriting of Securities Offerings: Investment banks help corporations and governments raise capital by issuing stocks, bonds, or other securities to investors.
- Merger and Acquisition Advisory: Investment banks provide strategic advice to companies looking to merge with or acquire other businesses, facilitating the deal-making process.
- Corporate Finance: Investment banks assist in structuring financial deals, managing risk, and optimizing capital structure to support the growth and expansion of businesses.
- Asset Management: Some investment banks offer asset management services to institutional and high-net-worth clients, helping them invest and grow their wealth.
Investment Horizon
Investment horizon refers to the length of time an investor expects to hold an investment before selling it. It is a crucial element in financial planning as it helps determine the appropriate investment strategy based on the investor’s goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
Short-Term Investment Horizon
Short-term investors typically have an investment horizon of less than one year. They focus on quick gains and often engage in active trading to capitalize on short-term market fluctuations. Strategies for optimizing returns in the short term include day trading, swing trading, and arbitrage opportunities.
Medium-Term Investment Horizon
Investors with a medium-term horizon usually hold investments for one to five years. They seek a balance between risk and reward, aiming for moderate growth over a relatively short period. Strategies for optimizing returns in the medium term include value investing, growth investing, and sector rotation based on economic trends.
Long-Term Investment Horizon
Long-term investors have a horizon of five years or more and focus on building wealth steadily over time. They are less concerned with short-term market fluctuations and more focused on the fundamentals of the investments. Strategies for optimizing returns in the long term include buy-and-hold investing, dividend investing, and dollar-cost averaging to benefit from compounding returns.
Investment Opportunities
Investment opportunities refer to various options available in the market where investors can allocate their funds to potentially earn returns. Evaluating these opportunities is essential to make informed decisions based on the balance of risk and return.
Types of Investment Opportunities
- Stock Market: Investing in individual stocks or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) can provide opportunities for capital appreciation.
- Real Estate: Investing in properties can yield rental income and potential appreciation in property value.
- Bonds: Fixed-income securities offer a steady stream of income through interest payments.
- Mutual Funds: Diversified investment vehicles managed by professionals that pool funds from multiple investors.
Evaluating Investment Opportunities
- Assessing Risk: Consider the level of risk associated with each investment opportunity, including market risk, credit risk, and liquidity risk.
- Examining Return Potential: Evaluate the potential returns that can be generated from each opportunity, taking into account historical performance and future growth prospects.
- Diversification: Spread investments across different asset classes to reduce risk and enhance overall portfolio returns.
Impact of Economic Conditions
Investment opportunities are influenced by economic conditions such as interest rates, inflation, and overall market sentiment. For example, during periods of economic growth, opportunities in sectors like technology and consumer discretionary may be more attractive, while defensive sectors like utilities and consumer staples may perform better during economic downturns.
Investment Strategy

Successful investment strategy is composed of various components that work together to achieve financial goals and maximize returns. Setting clear investment goals is crucial when developing a strategy, as it provides a roadmap for making informed decisions. Understanding the difference between active and passive investment strategies is also essential in determining the most suitable approach for individual investors.
Components of a Successful Investment Strategy
- Asset Allocation: Diversifying investments across different asset classes to manage risk and optimize returns.
- Risk Management: Assessing and mitigating risks associated with investments to protect capital.
- Research and Analysis: Conducting thorough research and analysis to identify investment opportunities and make informed decisions.
- Monitoring and Rebalancing: Regularly reviewing and adjusting the investment portfolio to align with financial goals and market conditions.
Importance of Setting Investment Goals
Setting clear investment goals helps investors define their objectives, whether it’s wealth accumulation, retirement planning, or funding education. By establishing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals, investors can tailor their investment strategy to meet their financial needs and aspirations.
Active vs. Passive Investment Strategies
- Active Strategy: Involves frequent buying and selling of investments in an attempt to outperform the market. Requires active management and research to identify opportunities.
- Passive Strategy: Involves investing in a diversified portfolio that mirrors a market index. Typically has lower fees and requires less hands-on management.
In conclusion, Value Investing Strategy Explained sheds light on the fundamental aspects of this investment approach, emphasizing the importance of strategic planning and goal-setting for successful outcomes in the financial realm.
FAQ
What is the core principle of value investing?
The core principle of value investing focuses on identifying undervalued stocks based on intrinsic value.
How do investment advisors create personalized plans?
Investment advisors create personalized plans by assessing the client’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
What is the difference between active and passive investment strategies?
Active investment strategies involve frequent buying and selling of assets to outperform the market, while passive strategies aim to match the returns of a specific market index.





